Uveitis Treatment
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle tissue layer of the eye. It is also known as "eye inflammation" among the public. Inflammation of not only the iris, ciliary and choroid regions of the uveal layer, but also the gel inside the eye is called uveitis.
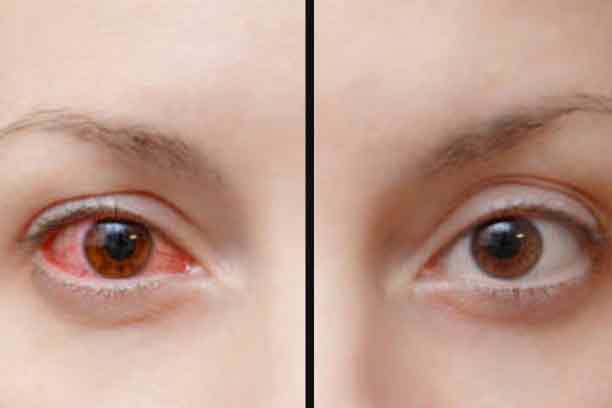
Although it generally affects people between the ages of 20 and 50, it can also be seen in children, although rarely. It may affect one or both eyes. Although the cause of inflammation is unknown in some cases, it is thought to be caused by immune system diseases, various infections and blows to the eye. Uveitisdisease can also be caused by genetic factors, viruses and bacteria.
Uveitis occurs with symptoms such as bloodshot eyes, blurred vision and pain. Since the main causes of the disease may be immune system diseases and infections, not only ophthalmologists but also physicians from different branches are involved in the patient's treatment process.
Since uveitis can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated, early diagnosis is essential. It is important for >uveitis treatment. Treatment begins with medications, and throughout the treatment process, other underlying diseases are examined and the process is continued according to these different findings.
SUBJECT TITLES
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis is known as eye inflammation and is in the class of autoimmune diseases. In other words, it occurs as a reaction of the body to itself. It is closely related to different diseases, and rheumatic diseases are closely related to uveitis, as it is one of the most common autoimmune diseases. That's why it is also known as "eye rheumatism" among the public.
There are 3 different layers in the human eye: vascular, nerve and support layer. The vascular layer in the middle of the eye and responsible for its nutrition is called uvea. Uvea consists of iris, choroid and ciliary body tissues.
The iris is the layer responsible for giving color to the eye, the choroid is responsible for nourishing the eye, and the ciliary body is the layer responsible for maintaining the shape of the lens, which is directly related to the iris and choroid. Inflammation in the uvea can affect all three layers mentioned.
What are the Causes and Risk Factors of Uveitis?
Uveitis is a disease that requires urgent intervention. Early diagnosis is important for treatment and prevention of possible complications. If left untreated, it can result in permanent blindness. In some cases, the disease responds to treatment and improves, while in other cases, although it improves, it can become chronic and recur.
The causes of uveitis are not fully known. The exact cause of uveitis cannot be determined in 30% or 40% of patients. Such cases are called idiopathic cases.
General reasons such as illness, eye impacts and injuries, previous eye surgeries, viruses, fungi and bacteria may cause the disease to occur.
As a result of research, the frequently identified causes of the disease are as follows:
Uveitis can occur due to various viruses and bacteria. Examples of these include syphilis, tuberculosis, brucellosis, herpes and HIV.
Behçet's disease may occur together with some systemic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,
Diseases related to the digestive system, such as Chorn disease and ulcerative colitis, can also be shown among the causes.
Also, some types of cancer, such as lymph cancer, affect the eye as a result of metastasis in the body and may cause uveitis. .
The risk factors for uveitis are as follows:
The risk is higher in people with a family history of uveitis.
Infection problems in different parts of the body increase the risk of disease occurrence.
A person's previous history of autoimmune or inflammatory disease is considered a serious risk factor.
Uveitis may also occur after eye injuries or the healing phase of eye injuries.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH OUR EYE DOCTORS
What are the symptoms of uveitis?
Uveitis symptoms, may vary depending on the area where the inflammation occurs, and may occur in one eye or both eyes simultaneously or with time differences.
If uveitis occurs in the front area of the eye, symptoms such as eye pain, discomfort from light and floating objects in front of the eye may occur. Additionally, if the inflammation has flowed heavily into the eye, blurred vision may occur.
These symptoms may sometimes be accompanied by changes in the pupil. Because due to inflammation, the iris may stick to the lens or its edges. This condition is accompanied by redness in the eyes.
If the inflammation occurs in the middle area, eye floaters and blurred vision may occur.
If uveitis occurs on the back surface of the eye. If it is removed, blurred vision and vision loss problems may occur along with sudden damage to the tissues. This type of uveitis can be detected as a result of in-depth examinations.
Other symptoms of uveitis are as follows:
- Hemorrhage in the eye,
- Dazzle,
- Watering in the eyes,
- Sudden flashes of light,
- Shrinkage of the pupil,
- Vasination and formation in the iris layer of the eye Symptoms such as edema
- Headache,
- Heterochromia (both eyes having different colors),
may also be observed.

The symptoms of the disease can sometimes appear suddenly and sometimes appear very slowly. If the disease affects an area related to central vision, a sudden decrease in vision may occur. In such a case, treatment should be started without delay. Because this may cause permanent vision loss.
What are the types of the disease?
Types of the disease are classified according to where they occur in the eye. These are:
Anterior uveitis is the type that occurs in the front part of the eye.
If it occurs in the middle part of the eye, it is called middle uveitis.
Panuveitis is the type that occurs in the three main parts of the eye.
Posterior uveitis (Intermediary) is the type that occurs in the back part of the eye.
How is the disease diagnosed?
In order to reveal and diagnose the cause of uveitis, PCR tests, blood tests and core imaging examinations can be performed in addition to general eye examination. Various consultations may be requested from doctors of other branches during the diagnosis phase of the disease.
If uveitis treatment is started late due to the late diagnosis of the disease, pupil deformity may occur for the patient. cataract and eye pressure risks. Each of these conditions negatively affects the patient's quality of life.
People who notice the symptoms of the disease should consult an ophthalmologist without delay. While the ophthalmologist performs various examinations and tests on the patient, he may also ask doctors from different units for the results of various tests for diagnosis.
There are different types of uveitis. While some of these varieties are easy to diagnose, some are difficult to diagnose. Although the disease is easily diagnosed, it is of critical importance whether the inflammation affects the back area of the eye. Although the disease can be diagnosed easily, the visual region and all the structures associated with this region should be examined with some tests such as angiography, optical coherence tomography and ultrasonography, both at the beginning and after the treatment.
How to Treat Uvetitis?
Uveitis treatment Firstly, medication is applied. Anti-inflammatory eye drops and ointments and antibiotics are used to relieve eye infection. If the inflammation is in all parts of the uvea, cortisone-containing medications can also be given to the patient.
Patients should protect their eyes from harsh sunlight during the treatment period to protect themselves from the harmful effects of the sun. Even if the disease progresses to advanced stages, vitrectomy surgery may be necessary at this point. If the error has caused serious damage to the eye structure, cataract, glaucoma and retina surgeries can also be performed. If uveitis is not treated, it may cause permanent vision loss.
The patient should not use medication according to his/her own wishes. Delay in diagnosing the disease may cause permanent vision loss or even blindness. The patient should not use medication on his own. The treatment process should definitely be progressed according to the advice of the doctors.
Uveitis does not occur due to a single disease. It progresses together with another disease. Therefore, from the moment the other disease is diagnosed, two different treatments are performed simultaneously. Since a doctor from a different branch will treat the disease occurring in another part of the body, both the ophthalmologist and the doctor from a different branch are in constant exchange of information for uveitis treatment.
It is early for uveitis. Permanent vision loss can be prevented with treatment that begins with diagnosis. Due to the possibility of relapse of the disease, the patient should undergo various examinations every 3 months after the treatment.