Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a serious eye problem that can be seen at any age, although it is frequently seen in middle-aged and older people. On average, it is seen in one in 10,000 people a year. It often develops suddenly. It is an eye problem that requires urgent intervention.
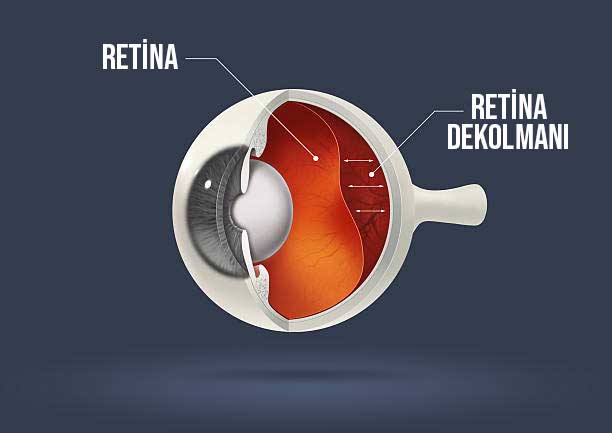
The retina layer, which consists of light-sensitive tissues that enable the light coming into our eyes from outside to be transmitted to the brain, has a very thin structure consisting of nerve cells and vessels feeding these cells.
It also covers the eyeball. The vitreous fluid covering the retina begins to pull on the retina due to changes in its structure over time due to aging and some other reasons. Holes and tears may occur as a result of the stresses experienced as a result.
Detachment is the separation of the retina from the pigment epithelial layer immediately behind it, to which it is attached, in the final stage, if these tears and holes are not intervened.
Delay in treatment. In this case, it may result in permanent or partial vision loss due to the nerve cells in the retina being deprived of oxygen and nutrients.
Retinal tear In the initial stages, black objects floating in the eye, blurring of vision and central vision loss may occur. While it can give symptoms. If sudden flashes of light are added to these symptoms, the possibility of retinal detachment increases.
It is important to diagnose the detachment in the early stages before it progresses. Depending on the different stages and types of the disease, drug treatment, intraocular injection, laser treatment or surgical intervention is required.
SUBJECT TITLES
What is Retinal Detachment?
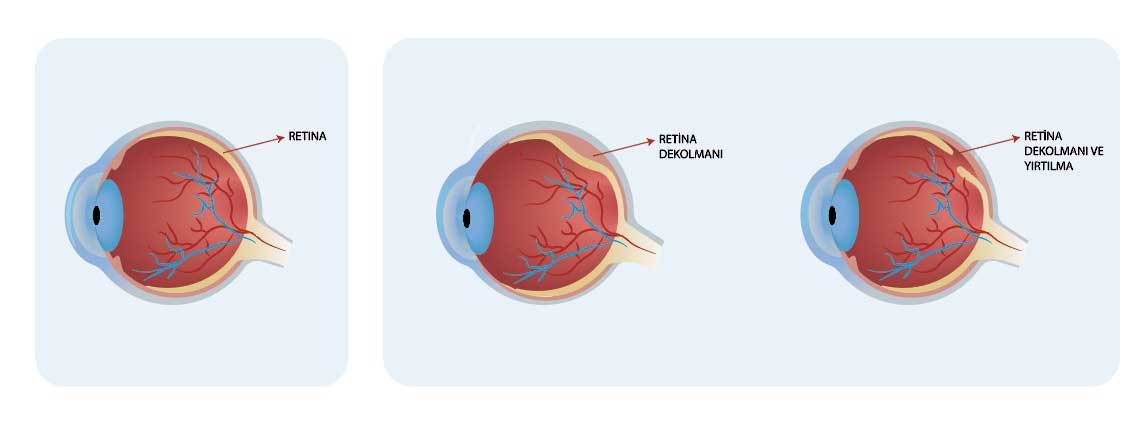
Retinal detachment (separation) is the separation of the retina from the wall on the inner surface of the eye to which it is attached. Retinal tears often occur in the processes before detachment occurs.
Retina covers the back of the eyeball like a sheet and contains billions of light-sensitive vision cells. and the retinal layer that is responsible for transmitting the light coming from outside and passing through the cornea and intraocular lens to the brain. This layer has a very thin and sensitive structure.
Various changes occur in the structure of the vitreous fluid that fills the inside of the eyeball with aging. This substance liquefies, shrinks, and begins to separate from the retina.
During this separation, it can stretch the retina and cause tears on its surface. If left untreated, these tears can grow over time and cause this layer to separate completely from the tissue to which it is attached due to fluid leakage under the retina.
The retina has a sensitive tissue that is difficult to nourish due to its structure. As a result of this decomposition, the nutrition of the tissues is impaired. If this situation is not treated immediately, permanent vision loss occurs.
Emergency treatment is required for initial level tears in order to prevent the problem of retinal detachment and minimize vision loss. If there is detachment, the patient should be taken into surgery without delay. Because the cells in this region are similar to brain cells in their structure. If the cell is lost, it cannot repair itself and permanent vision loss occurs in that area.
Due to the tears in question, if separation occurs while giving symptoms such as loss of central vision, blurred vision, objects flying in front of the eye
What Causes Retinal Detachment?
The separation of the retina from the pigment epithelium layer just below the nerve layer is called retinal detachment. In the stage before this separation, vitreous fluid begins to leak between both layers due to tears and holes formed on the retina. If this situation is not intervened, detachment occurs.
It is divided into 3 types according to its formation.
Detachment due to tear: The most common type of tear is the type of tear. are detachments. The vitreous fluid that fills the eye undergoes changes in its structure due to age or various eye traumas. As a result of these changes, it liquefies and shrinks.
During this shrinkage, it can stretch the retina and cause various tears. If the holes resulting from this tear are not noticed, fluid can enter through them and cause detachment in the future.
Tractional detachment: It can occur after diabetes, various eye traumas and some eye diseases. . In this type, retinal detachment occurs not due to any detachment but due to retraction. Various damages inside the eye cause shrinkage in this area. As a result of this pulling, detachment occurs if there is no intervention.
Exudative type detachment: It can occur as a result of eye inflammation, various traumas and eye diseases. There is no shrinkage or sudden punctures. It occurs as a result of fluid accumulation under the retina.
The fluid accumulated under the retina (serous exudation) pushes and lifts this layer. It can occur due to uveitis, macular degeneration and tumors in and behind the eye.
What are the Symptoms of Retinal Detachment and Tear?
Symptoms of retinal tear and retinal detachment develop rapidly and often appear suddenly. This is because retinal tear is a sudden and rapidly progressive condition. They require urgent intervention. If left untreated, they may result in separation and lead to permanent vision loss. Symptoms of retinal detachment and tear are as follows:
- Seeing floating objects in the eye and gradual increases in the size of these objects
- Experiencing shadows in peripheral vision
- Blurring of vision and Symptoms such as vision loss
- Seeing a black curtain moving from one direction to another in the visual field
- Sudden flashes of light
occur. If such symptoms are encountered, early intervention is important for treatment.
What are the Risk Factors?
Retinal tear is more common in older people, but can occur at any age. Especially patients with severe myopia, people who have had glaucoma or cataract surgery, people with various systemic diseases and people with a family history of retinal detachment are more prone to surface tears.

The reason for this is that in order for the tear to occur, there must be thinning on the surface of this area. This layer is thinner in people with severe myopia. In some eyes, since the retina is thin by nature, it can be stretched and ruptured as a result of various traumas.
With advanced age, there is a greater risk of ruptures due to the change in the structure of the vitreous fluid covering the inner surface of the eye.
How Are Detachments and Tears Diagnosed?
To detect tears and detachments, it is primarily performed by retinal examination. First, the pupils are dilated with the help of eye drops. After the pupils are dilated, the inner part of the eye is examined in detail by the ophthalmologist with the help of a biomicroscope. This method is one of the frequently used methods for diagnosing retinal diseases.
If there is a tear and detachment, it is detected in this way. In some cases, cataracts and intraocular bleeding make examinations in this area difficult. In such diseases, eye tomography and eye angiography can be performed.
Retinal Detachment and Tear Treatment
Detection of tears before retinal detachment occurs is important for treatment. A retinal tear causes symptoms such as floating objects in the eye, flashes of light, and narrowing of peripheral vision. If the person encounters these symptoms, he/she should consult an ophthalmologist without delay.
If a retinal tear is detected in the patient as a result of a detailed eye examination, it is usually treated with the laser method. Tears and holes formed in this area are sometimes seen in the macula. In this case, laser treatment cannot be applied, but surgery may be required.
If the beginning of detachment is detected as a result of holes and tears in this area as a result of the eye examination, surgery is required. Which surgery will be performed depends on the number of tears in this area, when they started, their size, shape and location.
Laser Treatment
Laser treatment of retinal tear problem is a treatment that can be performed in an office setting. Early diagnosis is very important to start treatment. Because for laser treatment, detachment must not have developed.
In laser treatment, the ophthalmologist creates small burns around the retinal tear with the help of laser beams. The scar tissue thus formed connects this area to the underlying tissue from which it was separated. The aim here is to prevent detachment by preventing fluid accumulation in the lower area. Patients with high degree myopia and patients who have had glaucoma or cataract surgery in the past should be closely monitored after laser treatment.
Retinal Detachment Surgery
If the type of detachment is tear and tractional, the treatment is surgical intervention. Collapse therapy, intraocular gas injection, and vitrectomy surgery are retinal surgery options for treatment of posterior vitreous detachment.
Introducing Gas into the Eye (Pneumatic Retinopexy):
It is a treatment method that can generally be applied to early diagnosed detachments. By injecting a gas bubble into the eye, it is aimed to prevent fluid leakage from the torn area. Afterwards, laser treatment is applied to close the torn area.
Collapse Treatment:
Without direct intervention inside the eye, scleral collapse is achieved by collapsing method through a silicone band from outside the eye. It is intended to be closed. It is mostly performed for cases detected early.
Vitrectomy Surgery:
In vitrectomy surgery, the eye fluid called vitreous is cleaned from under the retina and then the tears are closed with the laser method. is applied. The main purpose here is to withdraw the vitreous fluid that initiated the separation and leaked into the lower region. It is to be closed in a way that does not occur again.
Suitable patients can also have silicone oil or gas tamponade applied into the eye after vitrectomy surgery. There is no need to stay in the hospital after the surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some frequently asked questions regarding detachment and ruptures are as follows:
< strong>Can Retinal Tear Heal?
Retina, due to its structure, cannot reproduce and renew itself, just like brain cells. It is not possible to patch the torn area by stitching it. However, after the torn area is detected, it can be re-glued by laser treatment. Thus, it is aimed to minimize vision loss.
Does Retinal Tear Cause Blind?
Retinal tear and detachment is a sudden condition. If tears are not treated in time, they can cause detachment and cause permanent blindness. Timely intervention is important to prevent detachment and prevent vision loss from progressing and resulting in blindness.
