What is Eye Inflammation? What is Good for Eye Inflammation?
Eye inflammation is when microorganisms that cause infection settle in the eye and cause inflammation. Eye inflammation is a condition that can cause vision loss and life-threatening if not treated in time. The infection begins to show symptoms after hours or days. Eye inflammation is often confused with eyelid diseases such as styes and blepharitis. Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids and eyelashes and causes irritation. A stye is a pimple-like swelling that occurs at the base of the eyelashes and on the edges of the lids.
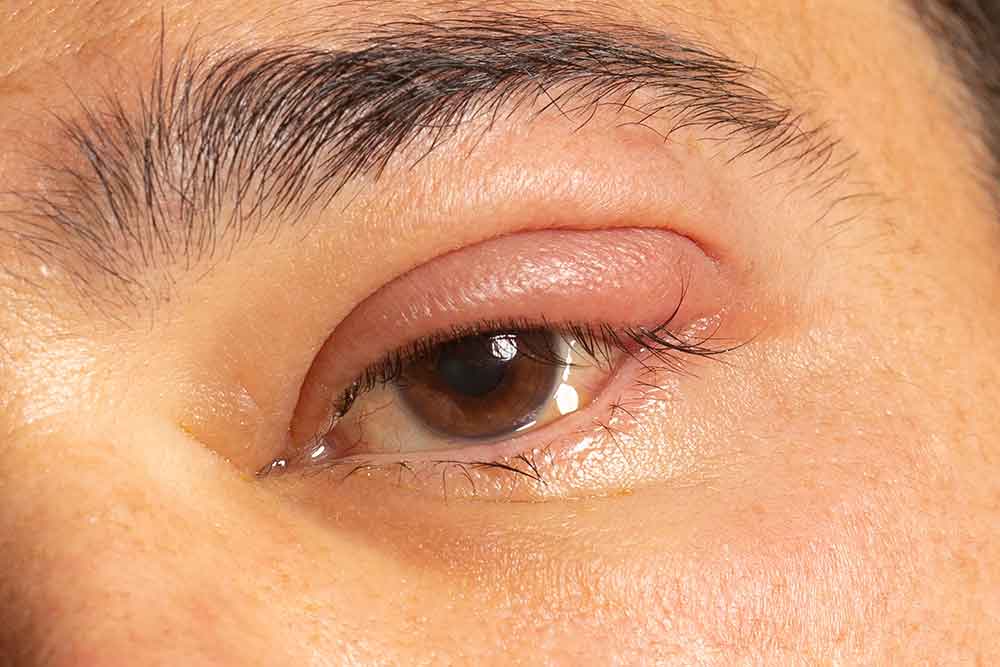
Ophthalmitis can be contagious, cause severe symptoms, and in some cases affect vision. If medical treatment is not provided, it can cause serious consequences and even be life-threatening. There are different types of inflammation, including uveitis, conjunctivitis, endophthalmitis, keratitis and orbital cellulitis, depending on the affected part. Inflammations that occur in the oil glands, eyelash bases and lids around the eyes are infections around the eyes. On the contrary, infections occurring inside the eye are listed as endophthalmitis, uveitis, conjunctivitis and keratitis. In this article, you can find answers to questions such as how intraocular inflammation occurs, what its symptoms and treatment are, and what is good for eye inflammation.
SUBJECT TITLES
What Causes Eye Inflammation?
Eye inflammation can occur for various reasons. Inflammation can be seen in different areas and can mainly be:
- Conjunctivitis: covering the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids It is an infection of the conjunctiva layer and is also known as “pink eye”. It is caused by bacteria, viruses, allergic reactions and exposure to chemicals and irritants such as chlorine found in swimming pools. It is highly contagious and can be easily transmitted from person to person.
- Uveitis: It is an infection of the middle layer called the uvea. It is usually caused by viruses such as Herpes, injuries, and autoimmune disorders such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. In severe cases, if left untreated, it may cause vision loss.
- Endophthalmitis: It is a severe inflammation of the fluid and tissues in the intraocular cavity. It may occur due to surgical procedures, bacterial, fungal infections and injuries. Endophthalmitis is an emergency and rapid diagnosis and treatment is essential.
- Keratitis: The transparent layer covering the pupil and colored iris is called cornea. Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea, and bacteria, viruses, fungi, injuries, and dirty water can cause the cornea to become inflamed. In addition, in contact lens wearers, not cleaning the lenses, expiring them, and sleeping with lenses increases the risk of developing keratitis.
- Ocular herpes: It is caused by the transmission of the herpes simplex virus (HPV). It can be transmitted through contact with someone who has an active HPV-1 infection, not through sexually transmitted HPV-2.
Eye Inflammation Symptoms
Eye inflammationmay occur for different reasons, but usually shows similar symptoms. Main symptoms:
- Pain or discomfort
- Redness and burning sensation in the eye
- Itching and swelling
- Dry or watery eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
Apart from the general symptoms of eye inflammation, some symptoms may be specific to that infection or some additional symptoms may be observed:
- Conjunctivitis manifests itself with eye redness. In addition to these symptoms, yellow, white or green discharge may be observed.
- In addition to redness and pain in uveitis, blurred vision, seeing floaters and sensitivity to light may be observed.
- In endophthalmitis, blurred vision, partial or complete In addition to vision loss, it may cause discharge and swelling.
- In the presence of keratitis, a feeling of having a foreign body in the eye may occur. It may also cause sensitivity to light, blurred vision and discharge.
- Ocular herpes may cause additional symptoms such as thick and watery discharge and eyelid inflammation.
Complications Due to Eye Inflammation
Various complications may occur depending on the type of eye inflammation. In some cases, eye inflammation may be the underlying cause of a condition such as corneal ulcer. In this context, the main cause of eye inflammation should be determined and urgent medical treatment should be initiated. Complications that may develop due to eye inflammation may include:
- Chronic corneal inflammation
- Retinal injury
- Retinal edema (macular edema)
- Cataract
- Optic nerve damage and permanent vision loss
Endophthalmitis is a severe eye inflammation and can lead to serious complications if immediate medical treatment is not provided. These serious complications include:
- Panophthalmia: Infection covering the eyeball
- Glaucoma: Damage to the optic nerves that extend to the brain
- Orbital cellulitis:Painful infection of the sebaceous glands and soft tissues that hold the eye in its socket
- Septicemia:Serious bloodstream infection, blood poisoning
- Phthisis bulbi: Severe eye damage
- Hypotonia: Decrease in intraocular pressure
If eye infection treatment is not provided on time, different complications may develop due to infection.
How Is Eye Inflammation Diagnosed?
Different tests may be required to diagnose eye inflammation. The presence of infection can be detected using physical examination and imaging techniques. Types of examinations include:
- In the physical examination, vision is tested and physical structure is checked. The response of the pupils to light is examined. Whether he has had previous surgery and his injury history are questioned. If there is a recent injury, ultrasound may be required to detect microorganism residues.
- Intraocular pressure is measured with tonometry examination.
- In slit lamp examination, eye structures are examined with the help of an intense light line.
- >
- In the ophthalmoscopy or fundoscopy test, the pupil is dilated and the back of the eye is examined with the help of light.
- A sample of aqueous/vitreous fluid or discharge is taken from the eyes with the help of a needle for examination in the laboratory. As a result of the test, it is determined whether there are bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
In eye inflammation, the treatment plan is determined according to the type of microorganism and the extent of the infection. Additionally, in some cases, your doctor may also request blood and urine samples.
How to Treat Eye Inflammation?
Eye inflammation is usually treated with medications. Additional treatments may be applied depending on the extent of the infection. These treatments are as follows:
- Conjunctivitis, if caused by bacteria, can be treated with antibiotic eye drops and ointments. If it is caused by a virus, antiviral drugs can be used. Symptoms begin to disappear within 1-2 weeks.
- Drops are given to relieve pain in the treatment of uveitis. Depending on the type of infection, antibiotics and antiviral drugs may be prescribed. Corticosteroid tablets (taken by mouth) or drops can be used to relieve eye inflammation. When treatment is not sufficient, corticosteroid injection may be necessary. In severe cases, when there is no response to corticosteroid treatment, other drugs that suppress the immune system can be used.
- Endophthalmitis is treated with antifungal and antibiotic drugs. Appropriate antibiotic treatment is started depending on the type of microorganism causing the infection. In the presence of severe eye inflammation and pain, steroid treatment can be started. Patients with poor vision may be given corticosteroids. Vitrectomy surgery is recommended in case of severe eye inflammation that limits the patient's vision. In the vitrectomy procedure, infectious and infected vitreous gel is removed and then antibiotic or antifungal medication is injected into the eye. Early vitrectomy helps preserve visual function by removing infected microorganisms and reducing the bacterial load.
- Antibiotic and antifungal eye drops or medications against bacteria and fungi are used in the treatment of keratitis. In the treatment of viral keratitis, antiviral drugs and drops are preferred to alleviate the infection.
- Eye drops, topical ointment and antiviral drugs can be used for the treatment of ocular herpes. If the inflammation spreads, corticosteroid eye drops may be preferred.
Depending on the severity of the eye inflammation, oral antibiotic treatment may be provided and injection may be necessary in some cases. Eye inflammation is treated with vitrectomy when necessary. Contact your doctor for the most appropriate treatment.
What is Good for Eye Inflammation?
Antibiotics and drops are usually prescribed to relieve eye inflammation. Antibiotic, antiviral and antifungal drugs are the main options that are good for inflammation. The question of what is good for eye inflammation is a matter of curiosity during the hygiene rules and care process. Eyes are areas susceptible to contamination through hands. For this reason, it is important to wash and disinfect hands frequently. Factors such as cosmetic products used and sleeping with make-up on may pave the way for infection, and therefore care must be taken. In addition, reducing the time spent in front of the screen and increasing the distance is another issue that should be taken into consideration. Although common practices such as salt water and tea bags are used for eye inflammation and eye disorders, do not use any products without consulting an ophthalmologist.
How to Prevent Eye Inflammation?
Reducing the risk of eye inflammation may be possible with some precautions and appropriate conditions:
- Always use protective glasses if you are in a job or environment where there is a risk of injury.
- Cleaning the dropper or container before using contact lenses
- Washing hands if eyes must be touched
- Using protective glasses during contact sports
- Using clean towels and washcloths every day
- Not sharing personal care items and cosmetic products
- Changing pillowcases frequently
- Making sure that the cosmetic products used are not old
- Post-operative instructions to comply with and take into account personal care recommendations
Regular control is required during the eye inflammation process and in the post-treatment period. It is important to pay attention to care and hygiene conditions, especially in cases such as eye surgeries or injections. In case of changes in vision, discomfort or pain, be sure to contact a relevant healthcare provider.
Tarih: 02/05/2023