Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a vision problem that occurs as a result of incompatible curvature of the cornea or the eye lens due to its structure. Due to its formation, it is a refractive error like Myopia and hypermetropia. As with other refractive errors, light cannot focus on the point on the retina where it should be focused. Depending on the type of astigmatism, it can focus in front or behind the retina. Thus, astigmatism patients cannot see clearly near or far depending on the area where the light falls on the retina.Astigmatism is derived from the Greek prefix "a" meaning deprivation and the combination of the words stigma meaning point. The origin of the word means that there is no focal point in Greek. It is an eye problem characterized by blurred vision for distance or near vision, or both.
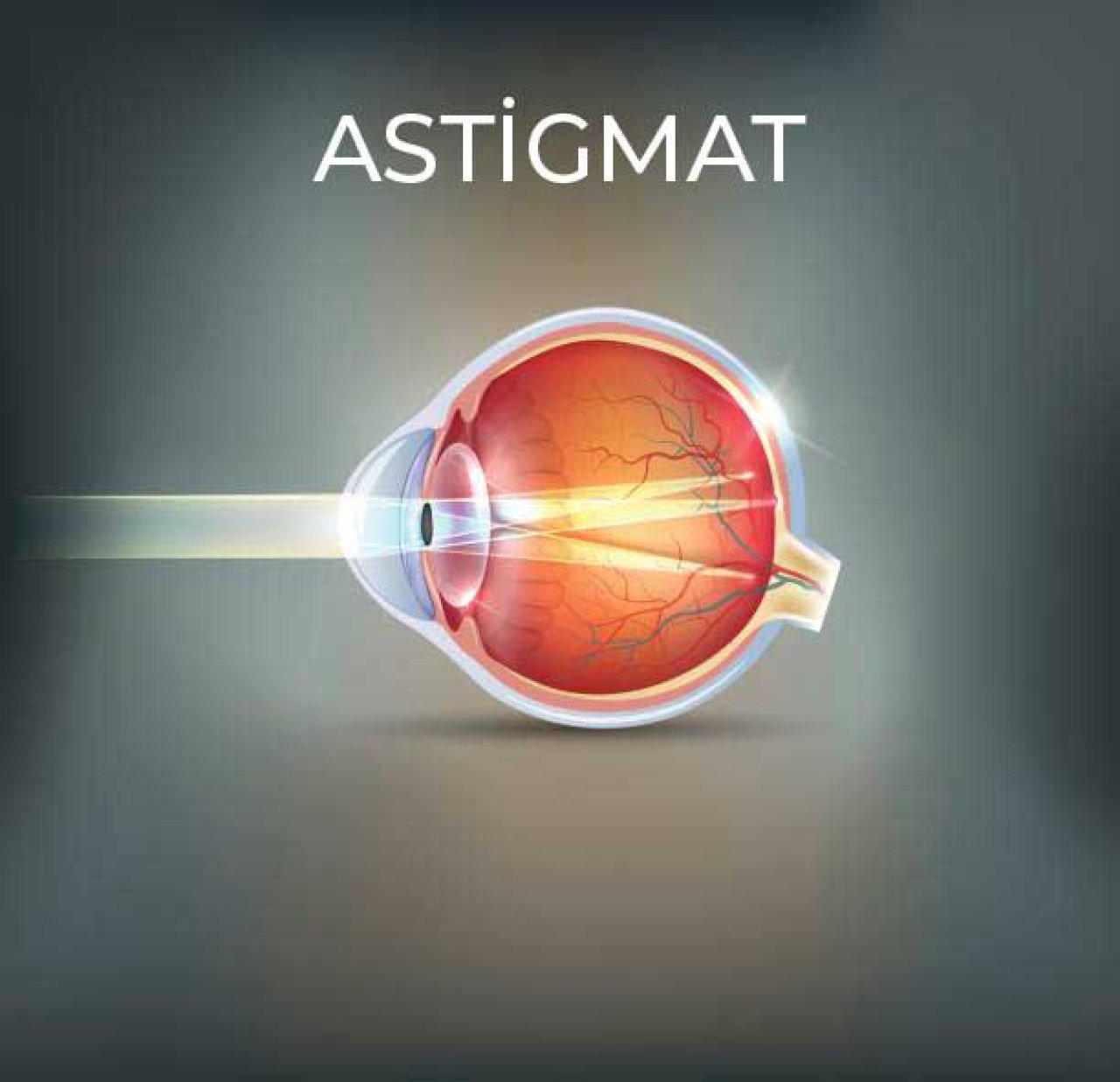
Astigmatism is one of the most common eye health problems around the world, which usually occurs at birth. From the moment the vision problem occurs, both distance and near vision are affected. The person sees distant objects and nearby objects blurry. Common symptoms are; It is blurred vision in one direction horizontally, vertically and diagonally.
Astigmatism symptoms are usually first noticed during school age. Symptoms can manifest themselves over any distance. From the moment the symptoms first appear, it is beneficial to consult an ophthalmologist for the success of the treatment, as in other eye problems.Astigmatism treatment, if the refractive problem affects the person's daily life and reduces the quality of life, glasses, contact lenses or eye It is performed by methods such as laser surgery. It is more common in people with a family history of astigmatism and in people who have undergone eye health-related surgery in the past.
SUBJECT TITLES
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is an eye defect caused by irregular curvatures on the surface of the cornea area on the front surface of the eye or the natural lens inside the eye. In a healthy eye, there is a perfectly round and proportional curvature between the cornea and the eye lens. The rays coming to the eye are refracted in the corneal layer on the front surface of the eye and pass through the intraocular lens and focus on the retina area. Thus, visual function is achieved in a healthy way. In an eye with astigmatism problem, the light bends incompatibly when reaching the retina due to the cornea or intraocular lens curving more steeply than the other. As a result of this situation, the light coming into the eye cannot be fully focused on the retina. Thus, blurred vision occurs for both distant and near objects, and the person's visual acuity is affected. Astigmatism means that the image is placed in front of or behind the retina and suddenly It is a refractive error that can fall on both points. In other words, the eye that has problems focusing at distance in myopia and near in hyperopia may experience problems in both distances in astigmatism.
What are the symptoms of astigmatism?
The most common astigmatism symptoms are as follows:
- Near, far and middle distance blurred vision, distortions in different points of the field of vision,
- A feeling of eye fatigue after reading or visual activities that require attention and eye pain,
- Headache,
- In advanced cases, double vision and squint in the eyes,
- Driving at night Difficulty when using it,
- Blurry in the vision of illuminated texts and signs accompanied by light beams,
- The desire to squint the eyes to see clearly,
- Blepharitis,
- Frequent formation of eye stye
How Does Astigmatism See?
“How does astigmatism see?” The question is wondered by many people. In an eye with an astigmatism problem, the rays cannot focus normally on the retina due to irregular curvature of the cornea or eye lens and refractive error occurs. People with astigmatism cannot see clearly from far or near distance. Sometimes, the problem of not being able to see both far and near clearly occurs together.
They see the objects and shapes they look at as blurry, with elongated and messy edges. They also see light rays around the edges of illuminated objects at night. However, among the symptoms of astigmatism, the deformity in vision is the characteristic feature of the disease.

What Causes Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is usually congenital. However, it can also occur after various eye surgeries and due to eye injuries. Another cause may be keratoconus, a disease in which the cornea gradually thins and the outermost part of the eye becomes domed. It is a less common refractive error than myopia and hyperopia. It does not progress due to various visual activities such as myopia and hyperopia, reading in dim light, or watching television closely.
Astigmatism is a refractive problem related to the eye focusing the light towards the retina. The parts that perform the visual function by refracting the light coming into the eye and focusing it on the retina are the cornea and the eye lens. Cornea is the name given to the transparent layer that forms the outermost layer of the eye and covers the front surface of the eye. The structure in the inner part of the eye that allows us to focus on both distant and near objects through various stretching movements is the eye lens.
A normal cornea and lens have a surface curvature that is proportional to each other. If the cornea has an elliptical shape instead of being round, the diameters of the lens and cornea are not equal. For this reason, the light entering the eye cannot be refracted properly and two different images are formed on the retina. These two different images overlap on the retina, resulting in blurred vision for both near and distant objects.
Astigmatism degrees generally vary between 0.25 and 4. Grades 4 and higher may be accompanied by a different vision problem.
How is Astigmatism Diagnosed? How is the test done?
Astigmatism can be detected by a detailed eye examination by an ophthalmologist. Astigmatism test is performed to determine the number of optical materials required to improve the patient's vision by measuring the ability of the eyes to focus on light. The following tests and examinations are used during this determination.
In the first stage of the diagnostic and treatment procedure, visual acuity testis applied. It is a routine test to help diagnose astigmatism. During the test, the person is asked to read certain letters and signs from a distance of 20 feet. As the value in the denominator decreases, visual acuity also decreases.
With the help of a phoropter, the ophthalmologist places a series of lenses in front of the patient's eyes and measures how the eyes focus on light. The measurement is made with the help of an illuminated hand tool called a retinoscope. The degree of astigmatism is diagnosed according to the person's answers by showing various letters and signs to the person, and the optical material that gives the person the clearest vision is determined.
In addition, the ophthalmologist measures the patient's corneal curvature with the help of keratometry. The ophthalmologist focuses a circle of light on the cornea and measures the reflection of the light. Corneal topography can also be used. Thus, the shape of the cornea is revealed and the curvature in certain areas of its surface is measured. Thanks to this measurement, it can be determined whether the patient is suitable for contact lenses.